Prove Vector Addition Is Associative
Associativeproperty of vector addition. We construct a parallelogram.

Linear Algebra Properties Of Vector Addition And Scalar Multiplication In The Plane Youtube
Im somewhat confused on why I am not getting the same answer for both like I should be.

Prove vector addition is associative. Homework Equations uvwuvw The Attempt at a Solution I cant figure out how to get the arrow on top of my work so I wrote it without it. Give an example of the associative property of vector addition using vectors in Cartesion form. Vector addition is commutative just like addition of real numbers.
Let these two vectors represent two adjacent sides of a parallelogram. 3 6 8 3 14 17. Hence 3 6 8 3 6 8 Distributive Property.
All elements of U 1 U 2 U 3 can be written as x y z Since U 1 U 2 U 3 is a vectorspace we have associativity therefore x y z x y z x y z showing that U 1 U 2 U 3 U 1 U 2 U 3 U 1 U 2 U 3 Please correct me if I am missing something. The law states that the sum of vectors remains same irrespective of their order or grouping in which they are arranged. Consider three vectors and.
The law states that the sum of vectors remains same irrespective of their order or grouping in which they are arranged. This fact is known as the ASSOCIATIVE LAW OF VECTOR ADDITION. This can be illustrated in the following two diagrams.
3 6 and 8. 3 6 8 3 6 8 9 8 17. The Associative Property of Vector addition states that for any three vectors veca vecb and vecc veca vecb vecc.
F g is the function with outputs defined by f gx fx gx. Let these two vectors represent two adjacent sides of a parallelogram. If you start from point Pyou end up at the same spot no matter whichdisplacement aor b you take first.
Vector Addition is Associative We also find that vector addition is associative that is u v w u v w. The head-to-tail rule yieldsvector cfor both a band b a. F left fmathrelf.
A b c a b c The rule works in all dimensions. This fact is known as the ASSOCIATIVE LAW OF VECTOR ADDITION. Notice that u v w and u v w have the same magnitude and direction and so they are equal.
We construct a parallelogram OACB as shown in the diagram. Applying head to tail rule to obtain the resultant of and Then finally again find the resultant of these three vectors. The distributive property is a rule that relates to the addition and multiplication.
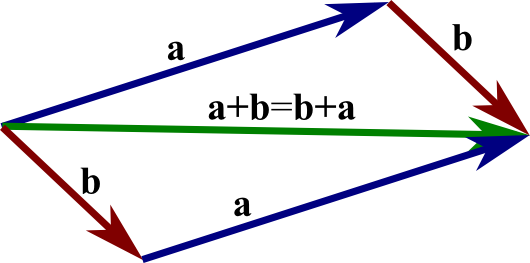
Show That the Following Numbers Follow the Associative Property of Addition. Consider two vectors and.
The inner product of two orthogonal vectors is 0. And the cos of the angle between two vectors is the inner product of those vectors divided by the norms of those two vectors. F g if and only if fx gx for all x ℂ.
A b b a. COMMUTATIVE LAW OF VECTOR ADDITION. The norm or length of a vector is the square root of the inner product of the vector with itself.
COMMUTATIVE LAW OF VECTOR ADDITION Consider two vectors and. Example VSF The vector space of functions Set. The diagonal OC represents the resultant vector From ab.
Then finally again find the resultant of these three vectors. Can you prove the associativity of vector addition Property AA. The result is the same in both cases.

Proof That Square Root Of 2 Is Irrational Algebra I Khan Academy Algebra I Algebra Math Videos

Linear Algebra Properties Of Vector Addition And Scalar Multiplication In The Plane Youtube

Proof Of Mathcal L V W Is A Vector Space Mathematics Stack Exchange

This Would Be A Great Video To Show To Introduce Students To Rational Exponents Exponents Eureka Math Mathematics
Https Sdss Bwdsb On Ca Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid 11506094
An Introduction To Vectors Math Insight












