Orthogonal Matrix Times Its Transpose
Consider a A2R n. Given Transpose of A Now multiply A and AT.
The Singular Value Decomposition Guzinta Math
Prove Q is orthogonal matrix.

Orthogonal matrix times its transpose. Start with a 3x3 matrix A and assume its orthogonal so that its 3 columns are 3-dimensional unit vectors which are orthogonal to each other. C D T D T C T. Then the matrix C 2 4v 1 v n 3 5 is an orthogonal matrix.
A square matrix with real numbers or values is termed as an orthogonal matrix if its transpose is equal to the inverse matrix of it. Thats the definition of an orthogonal matrix thus already being in your assumption that A is orthogonal. Finally Property 5 can be seen by noting that as Ais invertible I n AA 1I n I AA 1 A 1A Hence A 1 A.
A T A 1 T A 1 A T I T I. 4 ORTHOGONAL MATRICES AND THE TRANSPOSE One concludes that AB BA. Only the first item in the preceding list was discussed in the previous section and you can find formal proofs online for the other points.
Asked 4 years 5 months ago. In other words the product of a square orthogonal matrix and its transpose will always give an identity matrix. Conversely every diagonalizable matrix with eigenvalues contained in 1-1 and orthogonal eigenspaces is of that form.
The columns of any orthogonal matrix form an orthonormal basis of Rn. ΩΩ0 we can write OTOexp Ωexp Ωexp ΩΩexp 0 01 -1 transpose 10 Y -X 01. Then multiply A by its transpose.
Then AT 0 6 1 1 2 0 4 1 A. The orthogonal array Ai one gets bi such orthogonal arrays. Let A be an m n orthogonal matrix where a i is the i t h column vector.
For example if A 6 1 0 1 2 4. Where I is the n n identity matrix then A T is invertible and its inverse is B that is B A T 1. The i j t h element of A T A is.
Row times column or for matrix A ij and matrix B ij we have C ABwith C ij X k A ikB kj. Operations Involving Vectors and Matrices Suppose that you want to calculate Ax where A is an mxn matrix. Rotations are examples of orthogonal matrices.
Active 4 years 5 months ago. The following are equivalent 1 Ais orthogonal matrix. OTexp ΩTexp ΩTexp Ω which is the inverse of O.
If A is given by A cos sin. Using the fact that Ive just stated about its columns you should be able to prove that this product is the identity matrix. To see Property 4 use Ax y Axy xAy xAy xAy.
Since it is unitary the eigenspaces corresponding to 1 and to -1 are orthogonal. 7 Of course this implies that the number of columns of A is equal to the number of rows of B. In fact every orthogonal matrix C looks like this.
Since we have got the identity matrix at the end therefore the given matrix is orthogonal. Now transpose it to get. That -- take -- weve looked at products of three guys like that and taken their transpose and we got it back again.
To prove this suppose that Ais n k and Bis k m. Since Ω and Ω commute ie. Non Square Unitary Matrices.
Matrices can be multiplied. Transpose of a matrix De ned AT ij A ji. If youre assumed that A is already orthogonal then you dont need to prove that the columns are orthogonal unit vectors.
Well if Q is any n times n matrix with real entries with column vectors v_1 v_2 ldots v_n we have QT Q_ij sum_k1n QT_ik Q_kj sum_k1n Q_ki Q_kj sum_k1n v_i_k v_j_k langle v_i v_j rangle Now assume that Q is an orthogonal matrix ie its column vectors v_i are orthonormal. Here in the first equality we used the fact about transpose matrices that. If you can multiply together two matrices Aand B then ABT AT BT.
Recall that the transpose of a matrix is de ned by AT ij A ji. Unitary matrix times its transpose equals identity. The inverse of an orthogonal matrix is its transpose.
Determine if A is an orthogonal matrix. An orthogonal matrix is an invertible matrix Csuch that C 1 CT. Answered Jan 9 15 at 1906.
8 where ik is the Kronecker symbol. An orthogonal matrix times diagonal times the transpose of that orthogonal matrix. The eigenvalues of orthogonal matrix A are 1 or -1.
Let fv 1v ngbe an orthonormal basis for Rn. That is for othrog-. X j ij jk ik.
In other words to nd AT you switch the row and column indexing. In fact we have. If S is a real antisymmetric matrix then A I A1 S 1 is orthogonal.
To find if A is orthogonal multiply the matrix by its transpose to get Identity matrix. Suppose A is the square matrix with real values of order n n. Transposes and Matrix Products.
And of course everybody immediately says yes and if this is possible then thats clearly symmetric right. Equivalently a matrix A is orthogonal if its transpose is equal to its inverse. We claim that we can take A 1 T for this B.
In the following statement I dont understand the case for i j. If all such orthog-onal arrays are arranged side by side then one gets a matrix A with number of columns N X ET bNkO and number of rows q minqi q2 qm In the columns of any two-rowed submatrix of matrix A every ordered pair. An orthogonal matrix is a square matrix with real entries whose columns and rows are orthogonal unit vectors that is orthonormal vectors.
Ij is 1ij times the determinant of the minor matrix M obtained from of the matrix A by deleting the i-th row and the j-th column.
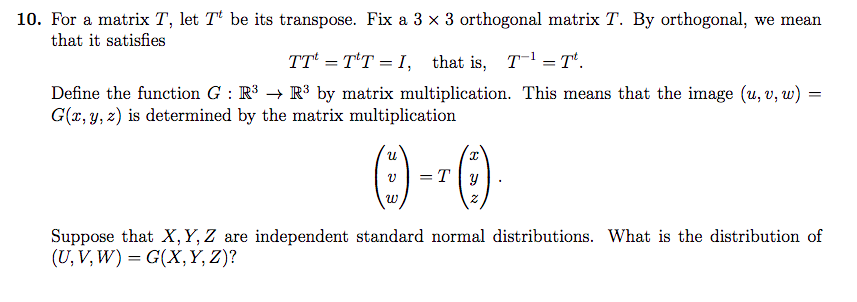
10 For A Matrix T Let Tt Be Its Transpose Fix A 3 Chegg Com

Linear Algebra 9 Properties Of Orthogonal Matrices By Jun Jun Devpblog Medium
What Is A Simple Way To Show That For Any Permutation Matrix P Its Inverse Equals Its Transpose Quora
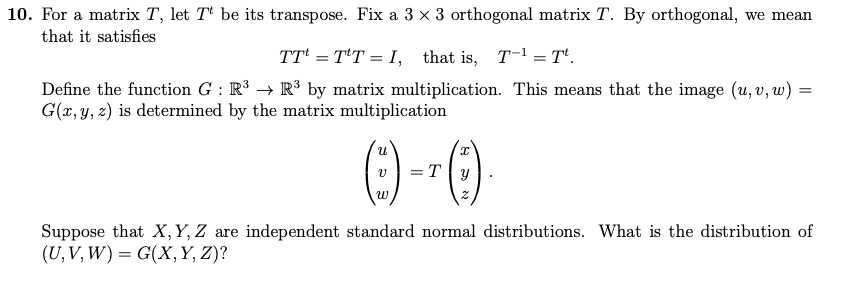
Solved 10 For A Matrix T Let T Be Its Transpose Fix A Chegg Com

Random Orthogonal Matrix Mathematica Stack Exchange

Linear Algebra 9 Properties Of Orthogonal Matrices By Jun Jun Devpblog Medium

Unit Vectors And Idempotent Matrices Problems In Mathematics
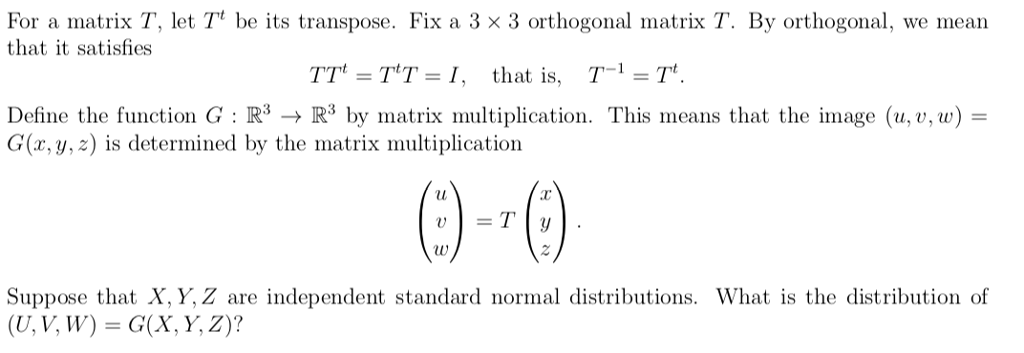
For A Matrix T Let Tt Be Its Transpose Fix A 3 3 Chegg Com

Linear Algebra Orthogonal Matrix Youtube

Example Using Orthogonal Change Of Basis Matrix To Find Transformation Matrix Video Khan Academy

Part 23 Orthonormal Vectors Orthogonal Matrices And Hadamard Matrix By Avnish Linear Algebra Medium

Orthogonal Matrix Definition Types Properties And Examples
What Are Orthogonal Matrices Quora
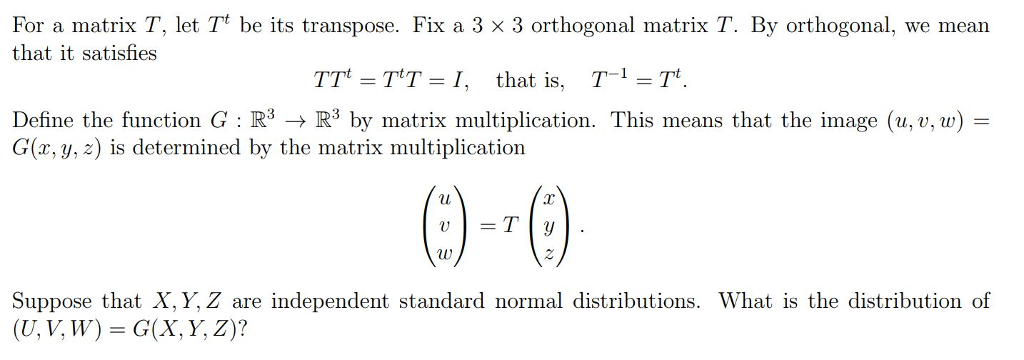
For A Matrix T Let T T Be Its Transpose Fix A 3 3 Chegg Com

Chapter 3 Linear Algebra February 26 Matrices 3

Part 23 Orthonormal Vectors Orthogonal Matrices And Hadamard Matrix By Avnish Linear Algebra Medium
Orthogonal Matrices Linear Algebra



