Is A Transpose A Always Symmetric
The inverse of a matrix is a matrix such that and equal the identity matrix. We know that a matrix to be symmetric its transpose must be equal to itself AAT whereas for a matrix to be orthogonal its product with its orthogonal must be an Identity matrix A.

Skew Symmetric Matrices Lesson Robot Academy
In linear algebra a symmetric matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its transpose.

Is a transpose a always symmetric. Ergo yes to both. Which implies that the product of a square matrix and its transpose is indeed symmetric. That is A is symmetric if.
Thus a symmetric matrix. Square matrix A is said to be skew-symmetric if aij aji for all i and j. Generally the symmetric matrix is defined as.
In more easier to. AA T A T AT By Algebraic Rule 4 for Transpose AAT. A matrix is called a symmetric matrix if its transpose is equal to the matrix itself.
You wont end up at the same conclusion. Thus a symmetric matrix. To know if a matrix is symmetric find the transpose of that matrix.
Formally because equal matrices have equal dimensions only square matrices can be symmetric. The transpose of a matrix is a matrix whose rows and columns are reversed. And we know that transpose of AB is given by AB BA Using this result take transpose of AA.
We know ABTBTAT so ATATAT ATTATA and hence ATA is always symmetric. We know that a matrix to be symmetric its transpose must be equal to itself AAT whereas for a matrix to be orthogonal its product with its orthogonal must be an Identity matrix A. In linear algebra a symmetric matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its transpose.
No not every symmetric matrix is an orthogonal matrix. By Algebraic Rule 1 for Transpose By the definition of symmetry AT A is symmetric. Why does the symmetry test fails here for medium-size-random matrices.
How do you know if a matrix is symmetric. In other words we can say that matrix A is said to be skew-symmetric if transpose of matrix A is equal to negative of matrix A ie AT A. That is A is skew-symmetric if.
We know ABTBTAT so ATATATATTATA and hence ATA is always symmetric. Its only true if A is a square matrix. If A is any symmetric matrix then A AT wwwmathcentreacuk 1 c mathcentre 2009.
Taking the transpose of each of these produces MT 4 1 1 9. Is a transpose a always symmetric. Because AxA transpose A transposexA thats why we cant say that A x A-transpose is invertible.
Only a square matrix is symmetric because in linear algebra equal matrices have equal dimensions. A zero square matrix is one such matrix which is clearly symmetric but not invertible. Displaystyle mathbf A operatorname T mathbf A A square matrix whose transpose is equal to its negative is called a skew-symmetric matrix.
A TAT A ATT By Algebraic Rule 4 for Transpose AT A. Idempotent idempotent matrix linear algebra symmetric matrix transpose Next story The Product of a Subgroup and a Normal Subgroup is a Subgroup Previous story A One-Line Proof that there are Infinitely Many Prime Numbers. It always works for small matrices 2020 etc.
A T A. No not every symmetric matrix is an orthogonal matrix. Give an Example of a Matrix Which is Symmetric but not Invertible.
B Show that AT A and AAT are both symmetric. The Product of a Matrix and its Transpose is Symmetric The product of any matrix square or rectangular and its transpose is always symmetric. If the transpose of that matrix is equal to itself it is a symmetric matrix.
Let be some square matrix and be its transpose. Transpose of AA AA T AA. You can prove it if you follow the same process for A x A-transpose.
By Algebraic Rule 1 for Transpose. Note that all the main diagonal elements in the skew-symmetric matrix are zero. Since it is indeed the case that the inverse of the product of a square matrix and its transpose also happens to be symmetric.
A square matrix whose transpose is equal to itself is called a symmetric matrix. Let A be an m n matrix. There is a mathematical theorem stating that a matrix A multiplied with its transpose yields a symmetric positive definite matrix thus leading to positive eigenvalues.
NT 2 7 3 7 9 4 3 4 7 Observe that when a matrix is symmetric as in these cases the matrix is equal to its transpose that is M MT and N NT. Lets take an example of a matrix.

Matrix Transposes And Symmetric Matrices By Adam Dhalla Medium
Symmetric Matrices Linear Algebra
Https Users Math Msu Edu Users Hhu 309 3091326 Pdf
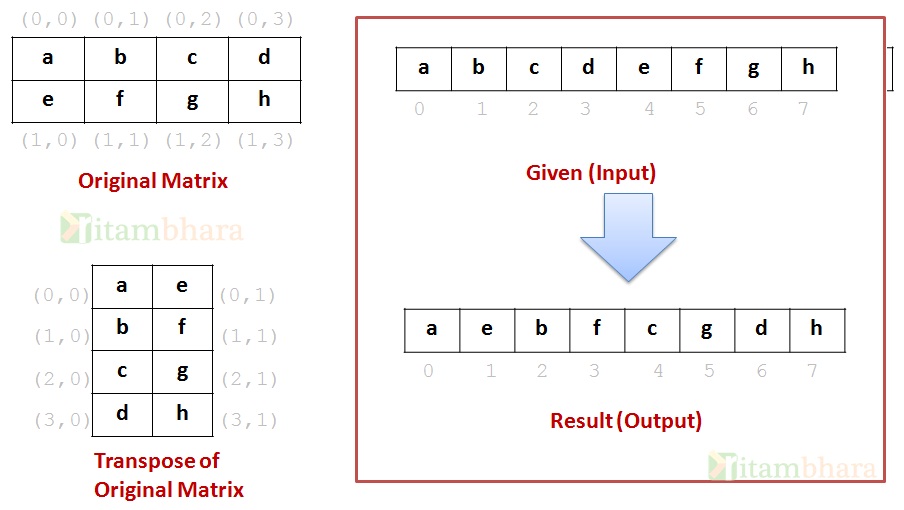
Transpose Of Non Symmetric Matrix Ritambhara Technologies

Why Transpose A Matrix Part 2 Symmetric Matrices Youtube

What Is The Difference Between Matrix Inverse And Matrix Transpose Quora

Matrix Transposes And Symmetric Matrices By Adam Dhalla Medium

Matrix Transposes And Symmetric Matrices By Adam Dhalla Medium
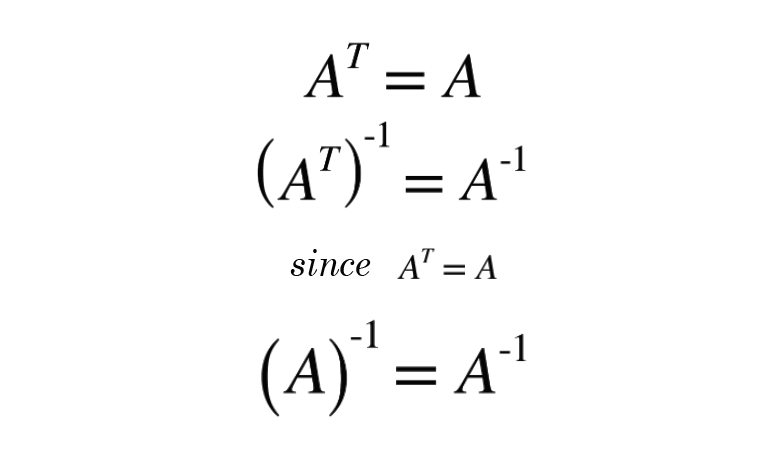
Matrix Transposes And Symmetric Matrices By Adam Dhalla Medium

Please Help Me With These Questions Only If You Know Chegg Com

2 Answer The Following Questions A Let B Be An N Chegg Com

Block Matrix Is Not Always Symmetric Product Of 2 Symmetric Matrices Is Not Symmetric Pr 2 7 7 Youtube
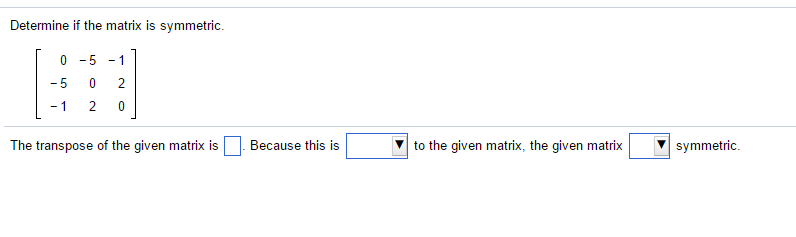
Solved Determine If The Matrix Is Symmetric 0 5 1 5 Chegg Com

1 7 Diagonal Triangular And Symmetric Matrices Ppt Download
Symmetric Matrices Linear Algebra

1 7 Diagonal Triangular And Symmetric Matrices Diagonal

If A Is A Skew Symmetric Matrix Then How Do You Prove That Aa Is Symmetric Quora

The Inverse Of An Invertible Symmetric Matrix Is A Symmetric Matrix Youtube


